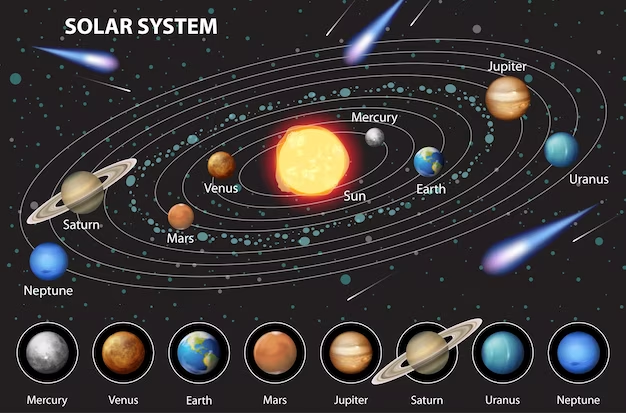

The solar system is a vast and fascinating region of space that consists of the Sun, its planetary system of eight planets and their moons, dwarf planets, asteroids, comets, and other objects, all bound together by gravitational forces. Here's a bit more detail about each component:
1. The Sun: At the heart of the solar system is the Sun, a star that provides light, heat, and energy to the planets and other celestial bodies. It contains more than 99% of the total mass of the solar system and is crucial for sustaining life on Earth.
2. Planets: There are eight recognized planets in the solar system, divided into two main categories:
#. Inner Planets (Terrestrial Planets): Mercury, Venus, Earth, and Mars. These are small, rocky planets with solid surfaces.
#. Outer Planets (Gas Giants): Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus, and Neptune. These are large planets primarily composed of hydrogen and helium, with thick atmospheres and no solid surfaces.
3. Dwarf Planets: Pluto was once considered the ninth planet but was reclassified as a dwarf planet in 2006 by the International Astronomical Union (IAU). Other dwarf planets in the solar system include Eris, Haumea, Makemake, and Ceres.
4. Moons: Many of the planets, as well as some dwarf planets, have natural satellites or moons orbiting them. For example, Earth has one moon, while Jupiter has over 70 known moons.
5. Asteroids: These are rocky bodies that orbit the Sun, primarily found in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. They vary greatly in size, from small boulders to several hundred kilometers across.
6. Comets: Comets are icy bodies that orbit the Sun in highly elliptical paths, often originating from the outer regions of the solar system. When they come close to the Sun, they develop a bright coma and sometimes a tail due to the sublimation of their icy materials.
7. Kuiper Belt and Oort Cloud: Beyond the orbit of Neptune lies the Kuiper Belt, a region of icy bodies similar to the asteroid belt but farther out. The Oort Cloud, even farther from the Sun, is a hypothesized spherical shell of icy objects that marks the outermost extent of the solar system.
Studying the solar system not only helps us understand our cosmic neighborhood but also provides insights into the formation and evolution of planetary systems throughout the universe.